Upper Body
Lower Body
General
Sports Related
Physiotherapy- Spine
Knowledge is Power.
True/False - Quiz: Do You Understand Orthopaedic Physiotherapy?
Information - Orthopaedic Physiotherapy
 Orthopaedic physiotherapy focuses on treating injuries or disorders of the skeletal system and associated joints, ligaments and muscles. An orthopaedic physiotherapist also helps patients with pre- and post-operative recovery and rehabilitation.
Orthopaedic physiotherapy focuses on treating injuries or disorders of the skeletal system and associated joints, ligaments and muscles. An orthopaedic physiotherapist also helps patients with pre- and post-operative recovery and rehabilitation.
Common Orthopaedic Conditions Physiotherapists Treat
ACL and MCL injuries: An ACL injury is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee, which is located in the middle of the knee joint. The ACL is one of the biggest stability structures of the knee. An MCL sprain is an injury to the medial collateral ligament of the knee. The medial collateral ligament is a structure that runs along the medial side of the knee.
Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common types of inflammatory arthritis. It’s a chronic, long-term disease that progresses over time. Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It’s caused when the cartilage on the ends of the bones wears down.
Fractures: A stress fracture is a small crack or severe bruising in a bone. Stress fractures of the foot are common in athletes, and are usually caused by overuse and repetitive activity. They also occur more commonly in people with osteoporosis, as they have weakened bones.
Hip/Knee Replacement: Arthritis is the most common reason that people undergo hip or knee replacement surgery. An orthopaedic surgeon will replace the damaged cartilage and bone with an artificial hip or knee joint.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic type of arthritis that affects the lower back, causing inflammation and resulting in pain and stiffness.
Orthopaedic Physiotherapy Techniques
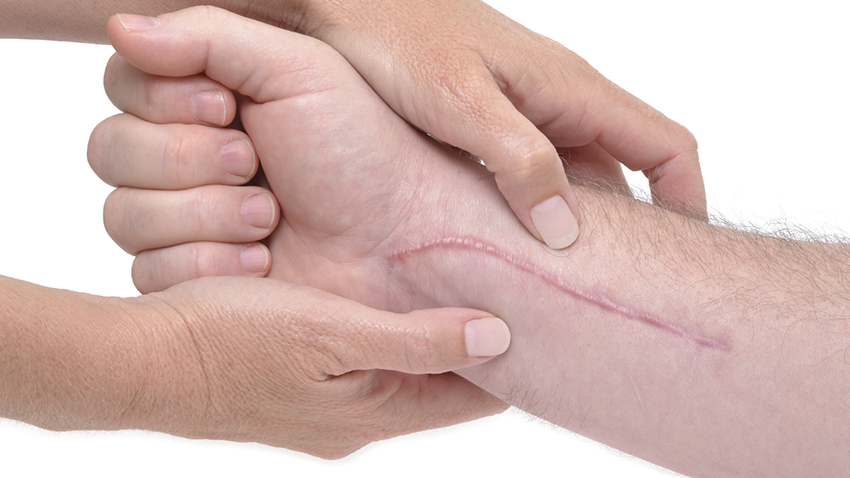 Manual therapy: A hands-on technique to mobilise and manipulate joints to reduce pain and increase range of motion.
Manual therapy: A hands-on technique to mobilise and manipulate joints to reduce pain and increase range of motion.
Myofascial release: Using gentle manual pressure, the physiotherapist will massage and stretch points in your fascia, which is the connective tissue that supports your organs, bones, muscles, nerves and blood vessels.
Ultrasound: Sound waves generate heat deep in the body, loosening up tissues so they’re better prepared for exercise or manual therapy.
Range-of-motion exercises: You’ll do some assisted exercises and exercise at home. Physiotherapists will recommend exercise after virtually any injury. Your physiotherapist will show you strengthening exercises based on your condition and current health.
Kinesio taping: This flexible, colourful tape is applied to the skin to stabilize muscles and joints while you undergo physiotherapy treatment.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you'd like more information on orthopaedic physiotherapy.
Visit HealthChoicesFirst.com for more videos and resources on orthopedics.
Print this Action Plan and check off items that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider
-
Orthopaedic physiotherapy focuses on treating injuries or disorders of the skeletal system and associated joints, ligaments and muscles.
-
An orthopaedic physiotherapist helps patients with pre- and post-operative recovery and rehabilitation.
-
Physiotherapists may help patients with orthopaedic conditions such as ACL/MCL injuries, arthritis, fractures, hip/knee replacement and ankylosing spondylitis.
-
Physiotherapists often use manual therapy, a hands-on technique to mobilise and manipulate joints to reduce pain and increase range of motion.
-
You’ll do some assisted exercises and exercise at home. Physiotherapists will recommend exercise after virtually any injury. Your physiotherapist will show you strengthening exercises based on your condition and current health.

